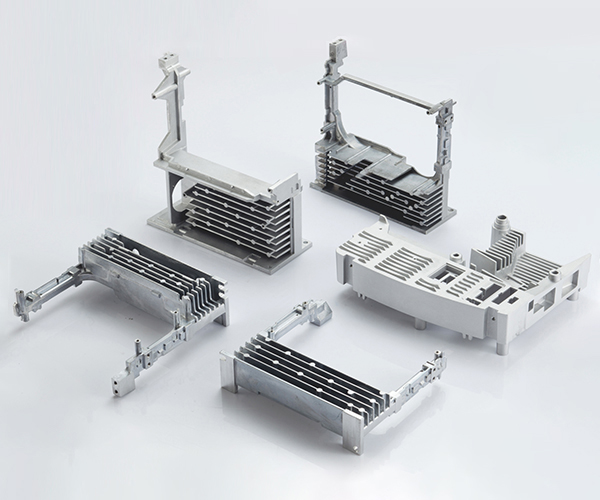
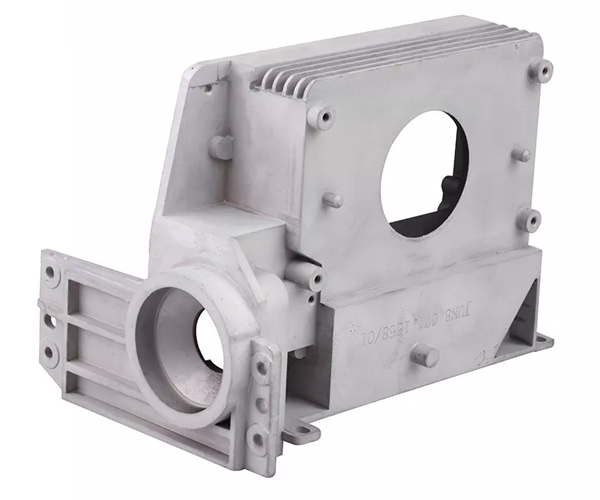
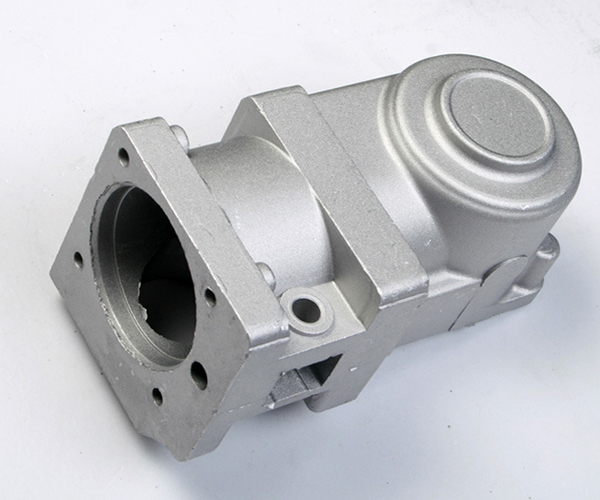
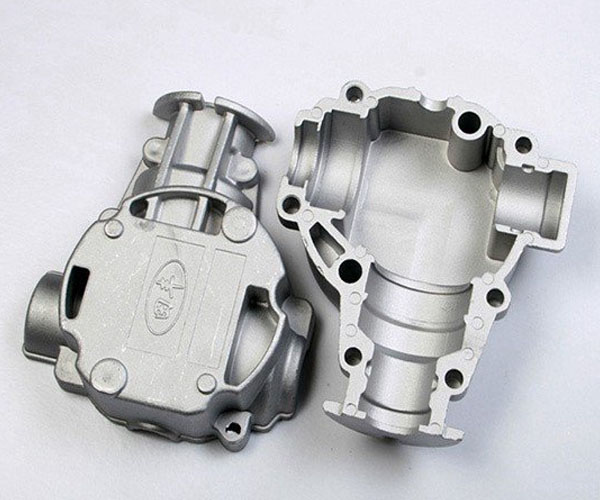
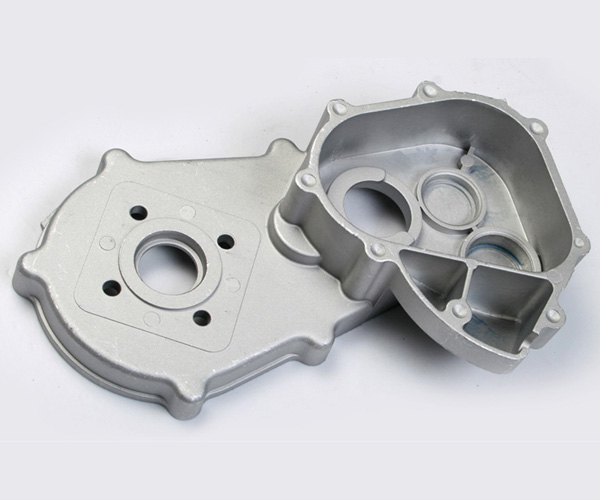
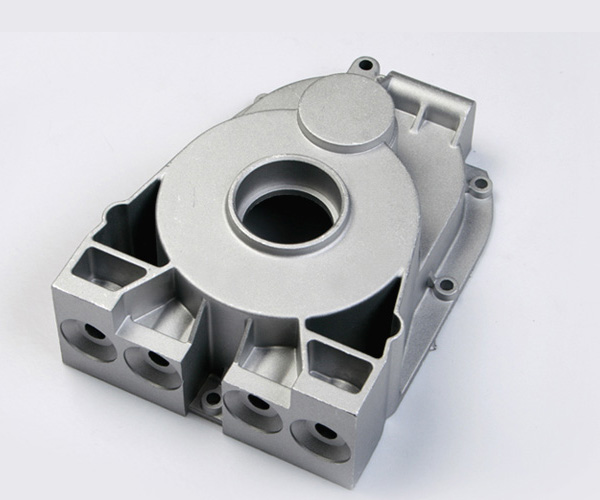
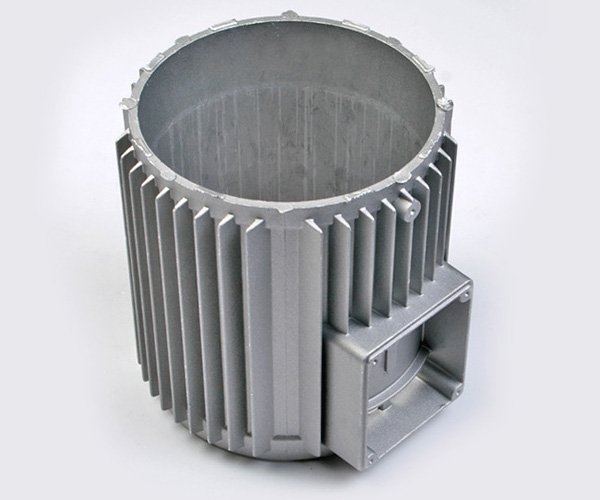
Key design factors for aluminium Die Casting
Key design factors for aluminium die casting. Here are some additional points that can improve their effectiveness: 1.Material selection: Selection of the right aluminium alloy is critical to achieving the required mechanical properties, surface finish and overall performance of the final part. Factors such as strength, corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity should be considered when